The law of demand illustrates that as
a. price decreases, demand increases.
b. price increases, quantity demanded increases.
c. price decreases, quantity supplied increases.
d. price decreases, quantity demanded increases.
d. price decreases, quantity demanded increases.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as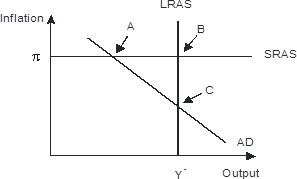
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Gene's Car Wash is a natural monopoly. To wash 100 cars a week, if Gene is unregulated, he would charge a price of $10. Gene's long-run average cost for washing 100 cars is $8, his average variable cost is $6, and his marginal cost is constant at $4
If Gene was regulated using a marginal cost pricing rule, the price he would be allowed to charge to wash 100 cars is A) $10. B) $8. C) $6. D) $4.
Changes in the interest rate bring the money market into equilibrium according to
a. both liquidity preference theory and classical theory. b. neither liquidity preference theory nor classical theory. c. liquidity preference theory, but not classical theory. d. classical theory, but not liquidity preference theory.
A product that was produced in 2009 and not sold until 2010 is counted as part of GDP in 2010.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)