If Bank A borrows from Bank B, reserves in the banking system __________. If Bank A borrows from the Fed, reserves in the banking system __________
A) rise; fall
B) fall; remain unchanged
C) remain unchanged; remain unchanged
D) remain unchanged; rise
E) rise; remain unchanged
D
You might also like to view...
Assume that the government has a target value, X, for the current account surplus
(a) What is the goal of external balance? (b) Assume that we are dealing with only the short run, what are the values of P and P?? (c) Given fixed P and P , what would happen if E rises? (d) Given P and P , what would happen if T decreases, i.e., an expansionary fiscal policy? (e) Given P and P , what would happen if G increases, i.e., an expansionary fiscal policy? (f) Given all of the above, what is the relation between the exchange rate, E, and fiscal ease, i.e., an increase in G or a reduction in T? (g) Assume that the economy is in external balance. What will happen if the government maintains its current account at X, but devaluates the domestic currency? (h) Assume that the economy is at external balance. What will happen if the government raises E? (i) Assume that the economy is at external balance. What will happen if the government lowers E?
The goal of endogenous growth theory is to explain ________
A) supply and demand in individual markets B) the causes of technological advance C) the business cycle D) the relationship between economic growth and the rates of inflation and unemployment
The lag before the full effects of monetary policy on inflation are felt is longer than the lag before its effects on real output and unemployment are felt
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the diagram, where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources. The total output of this firm will cease to expand:
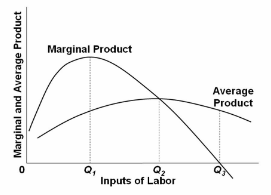
A. if a labor force in excess of Q 1 is employed.
B. if a labor force in excess of Q 2 is employed.
C. if a labor force in excess of Q 3 is employed.
D. only if the marginal product curve becomes negative at all levels of output.