Understand the purpose of the following mechatronic system and recommend an appropriate sensor and actuator to carry out the specified task.
a. Temperature Control System
Purpose: To maintain the temperature of a confined space at the specified temperature. (Hint: Decide how to sense the temperature. Decide how to increase or decrease temperature.)
b. Anti-lock Braking System
Purpose: To prevent wheel lock-up by automatically modulating the brake pressure during an emergency stop. (Hint: Decide how to sense that the wheels are locked (i.e.: the wheels are not rolling). Decide how to apply or release brakes.)
What will be an ideal response?
a. Temperature Control System
To control the temperature of a confined space at a specified temperature, an example of a thermostat could be used to control the furnace supplying heat. The thermostat would be programmed with a specific “deadband”, or a range of acceptable temperature for the room. If the temperature of the space drops below the deadband of the thermostat, the thermostat turns the furnace on. Once the thermostat senses that the furnace has heated the space enough, it then shuts the furnace “off”. Having a deadband rather than a single control temperature minimizes the amount of start-ups and shut-downs of the system.
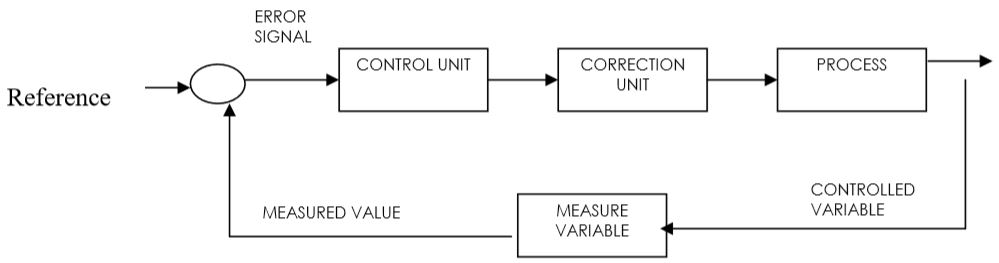
For a thermostatically controlled room heater:
Controlled variable = room temp.
Reference value = required room temp.
Error signal = difference between measured & required temp.
Correction unit = regulator
Process = heating Measuring
device = thermostat
b. Anti-lock Braking System
An anti-lock braking system, or ABS, is a safety system which prevents the wheels on a motor vehicle from locking up (or ceasing to rotate) while braking. In the automobiles fitted with ABS systems, a rotating road wheel allows the driver to maintain steering control under heavy braking by preventing a skid and allowing the wheels to continue interacting with the road surface as directed by driver steering inputs.
In the anti-lock braking system, a sensor at each wheel would need to be used to check the status of the wheels. If the sensor determines that the wheel has stopped spinning during heavy braking, it would then need to rapidly vary the brake pressure to stop the wheels from locking. A simple counting sensor could be used to track the rotation of the wheels. For example, if the sensor stops counting the rotations, this would turn the antilock braking system on. A high speed valve or hydraulic actuator would need to be utilized to rapidly change the brake pressure to get the wheels spinning again.
The modern ABS system applies individual brake pressure to all four wheels through a control system of hub mounted sensors and a dedicated micro-controller. A typical ABS is composed of a central electronic control unit (ECU), four wheel speed sensors — one for each wheel — and two or more hydraulic valves within the brake hydraulics. The ECU constantly monitors the rotational speed of each wheel, and when it detects a wh rotating significantly slower than the others — a condition indicative of impending wheel lock — it actuates the valves to reduce hydraulic pressure to the brake at the affected wheel, thus reducing the braking force on that wheel. The wheel then turns faster when the ECU detects it is turning significantly faster than the others, brake hydraulic pressure to the wheel is increased so the braking force is reapplied and the wheel slows. This process is repeated continuously, and can be detected by the driver via the brake pedal.
You might also like to view...
Another name for the wall-area method is the _____ method.
A. simple estimation B. wall-minus-openings C. Multiplication D. square foot
A frequency ________ is a circuit that can measure and display the frequency of a signal
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Which of the following are function(s) of slack adjusters used on truck air brake systems?
A. multiply force applied to the S-cams B. define shoe to drum freeplay C. convert linear force to rotational force D. all of the above
What are three common types of pins?
What will be an ideal response?