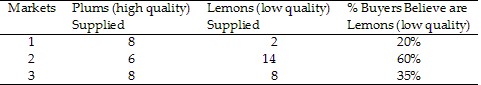
 Table 14.2Refer to Table 14.2. In which market do buyers underestimate the chance of getting a lemon?
Table 14.2Refer to Table 14.2. In which market do buyers underestimate the chance of getting a lemon?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Someone who turns down an opportunity to purchase a Bible for $5 and then immediately pays $5 to attend a movie thereby expects to obtain more satisfaction from seeing the movie than from
A) cultivating the spiritual life. B) deepening his religious faith. C) owning the Bible just offered to him. D) reading the Bible.
Since a monopolistically competitive firm faces a ____ demand curve, it will always operate ____ in long-run equilibrium
a. perfectly elastic; with excess capacity b. downward-sloping; with excess capacity c. downward-sloping; at an economically efficient scale d. perfectly inelastic; at an economically efficient scale
When the nation of Worldova allows trade and becomes an exporter of silk,
a. residents of Worldova who produce silk become worse off; residents of Worldova who buy silk become better off; and the economic well-being of Worldova rises. b. residents of Worldova who produce silk become worse off; residents of Worldova who buy silk become better off; and the economic well-being of Worldova falls. c. residents of Worldova who produce silk become better off; residents of Worldova who buy silk become worse off; and the economic well-being of Worldova rises. d. residents of Worldova who produce silk become better off; residents of Worldova who buy silk become worse off; and the economic well-being of Worldova falls.
Public goods are characterized by the free-rider problem because
A. public goods are characterized by the principle of rival consumption. B. public goods can easily be subdivided into small units. C. no one can be excluded from the benefits of public goods once they are produced. D. public goods are usually things that people really do not want to consume.