Many countries in sub-Saharan Africa have very low labor productivities in many sectors, for example in manufacturing and agriculture
They often despair of even trying to attempt to build their industries unless it is done in an autarkic context, behind protectionist walls because they do not believe they can compete with more productive industries abroad. Discuss this issue in the context of the Ricardian model of comparative advantage.
The Ricardian model of comparative advantage argues that every country must have a comparative advantage in some product (assuming there are more products than countries). However, the Ricardian model is not a growth model, and cannot be used to identify growth modes or linkages.
You might also like to view...
Use the figure below to answer the following question.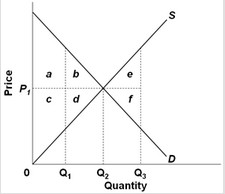 If actual production and consumption occur at Q2
If actual production and consumption occur at Q2
A. missing surplus of a + b + c + d occurs. B. economic surplus is maximized. C. missing surplus of e + f occurs. D. missing surplus of a + c occurs.
Autonomous expenditure is expenditure that is
A) influenced by the interest rate. B) not influenced by the interest rate. C) not influenced by real GDP. D) not influenced by the price level. E) influenced by real GDP.
Producers supply larger quantities of any good at higher prices because:
a. prices signal product quality.
b. higher prices attract resources from other uses.
c. people are naturally lazy and refuse to give up their leisure.
d. price and quantity supplied are inversely related.
e. of the law of decreasing opportunity cost.
The government often intervenes when private markets fail to provide an optimal level of certain goods and services. For example, the government imposes an excise tax on gasoline to account for the negative externality that drivers impose on one another. Why might the private market not reach the socially optimal level of traffic without the help of government?