Refer to the data. Average product is at a maximum when:
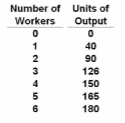
Answer the question on the basis of the following output data for a firm. Assume that the amounts of all nonlabor resources are fixed.
A. five workers are hired.
B. four workers are hired.
C. three workers are hired.
D. two workers are hired.
D. two workers are hired.
You might also like to view...
Mexico and the members of OPEC produce crude oil. Realizing that it would be in their best interests to form an agreement on production goals, a meeting is arranged and an informal, verbal agreement is reached. If both Mexico and OPEC abide by the agreement, then OPEC's profit will be $200 million and Mexico's profit will be $100 million. If both Mexico and OPEC cheat on the agreement, then OPEC's profit will be $175 million and Mexico's profit will be $80 million. If only OPEC cheats, then OPEC's profit will be $185 million, and Mexico's profit will be $60 million. If only Mexico cheats, then Mexico's profit will be $110 million, and OPEC's profit will be $150 million. You may find it helpful to fill in the payoff matrix below. src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__rrr0818190951__f1q380g1.jpg" alt="" style="vertical-align: 0.0px;" height="203" width="377" />To Mexico, the payoff to cheating is either:
A. $80 million or $110 million.
B. $150 million or $200 million.
C. $100 million or $110 million.
D. $60 million or $100 million.
In real business cycle models, business cycles are caused by ______, while in new Keynesian model, business cycles are caused by ________
a. aggregate demand; aggregate demand b. aggregate demand; aggregate supply. c. aggregate supply; aggregate demand. d. fiscal policy; monetary policy
Consider a duopoly with homogeneous products, where two competing firms pick price (Bertrand duopoly). In this chapter you learned that both firms will choose price equal to the marginal cost (MC). But what happens if the the two firms have unequal marginal costs? Suppose that Dogwood has MC = $40andRosePetalhasMC = $25. Assume firms can set prices such as $29.99.
A. Explain why it is not a Nash equilibrium for both firms to set a high price such as $60. B. Explain why it is not a Nash equilibrium for both firms to set a price equal to the lower marginal cost of $25. C. Explain why it is not a Nash equilibrium for each firm to set a price equal to their respective marginal costs. D. What is a Nash equilibrium? Which firm sells? At what price?
The long-run aggregate supply curve:
A. never moves. B. shifts right when the economy experiences economic growth. C. shifts left when the economy experiences economic growth. D. is affected by the price level.