An asteroid approaches Earth so that when it is very far away it is traveling with a speed of 6500 m/s along a line that would miss the center of Earth by 8,500,000 m
Because of the gravitational attraction of Earth, it departs from this straight line and curves towards Earth, colliding with it. In what direction, below the local horizontal, is the asteroid traveling when it hits Earth? The mass of Earth is 5.97 × 1024 kg and G = 6.67 x 10-11 N•m2/kg2. A) 48°
B) 58°
C) 68°
D) 78°
E) 88°
A
You might also like to view...
An automobile moving along a straight track changes its velocity from 40 m/s to 80 m/s in a distance of 200 m. What is the (constant) acceleration of the vehicle during this time?
a. 8.0 m/s b. 9.6 m/s c. 12 m/s d. 6.9 m/s e. 0.20 m/s
Frank says that if you release the string when swinging a ball in a horizontal circle, the ball flies out in the radial direction defined by the string at the instant you release the ball. John says that it flies out along a tangent line perpendicular to the string, and that it then drops straight down to the ground. Which one, if either, is correct?
a. Frank, because the centrifugal force is no longer counteracted by the string. b. Frank, because balls naturally fly straight out. c. John, because there is no centrifugal force. d. John, because balls fall straight down when released. e. Neither, because although there is no centrifugal force, and the ball's velocity is tangent to the circle at the instant of release, the ball then follows a parabolic trajectory.
The tallest spot on Earth is Mt. Everest, which is 8850 m above sea level. If the radius of the Earth to sea level is 6370 km, how much does the magnitude of g change between sea level and the top of Mt. Everest?
A. 0.0030 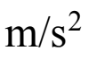
B. 0.020 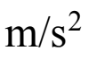
C. 0.035 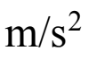
D. 0.025 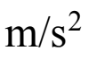
E. 0.030 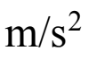
After 8.0 years have elapsed, 15/16 of a sample of a specific radionuclide has decayed. What is the half-life of the radionuclide?