If potential output is unknown:
A. factor prices are more likely to change.
B. we can still determine how the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift.
C. we cannot determine precisely how the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift.
D. factor prices are less likely to change.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
One reason why firms in monopolistically competitive markets earn zero profit in the long run is because
a. product differentiation disappears b. barriers to entry become prohibitive c. the price elasticity of demand for each firm falls to zero d. so many firms enter the market that each firm's demand curve eventually becomes tangent to the firm's ATC curve e. each firm's ATC curve shifts upward to eventually become tangent to its demand curve
M2 includes:
a. Currency in circulation + Checking Accounts b. Checking accounts plus Deposits at the central bank. c. Currency in circulation + Reserves of financial intermediaries (e.g., banks) + Checking Accounts + Near Money. d. Currency in circulation + Checking Accounts + Near Money. e. Currency in circulation + Cash inside financial intermediaries + Deposits at the central bank + Checking Accounts + Near Money.
In the United States in 2015, consumption represented slightly less than
a. 60 percent of GDP. b. 70 percent of GDP. c. 80 percent of GDP. d. 90 percent of GDP.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 32.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.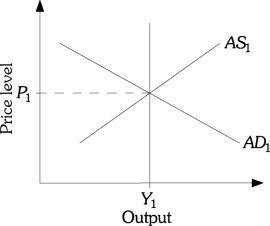 Figure 32.2Refer to Figure 32.2. According to monetarists, an expansionary fiscal policy in the long run and after all the adjustments have been made
Figure 32.2Refer to Figure 32.2. According to monetarists, an expansionary fiscal policy in the long run and after all the adjustments have been made
A. increases the price level above P1, but does not change equilibrium output. B. increases equilibrium output above Y1 and decreases the price level below P1. C. does not increase equilibrium output or the price level. D. increases equilibrium output above Y1, but does not change the price level.