Refer to the graph. Other things equal, an increase in labor productivity would cause a:
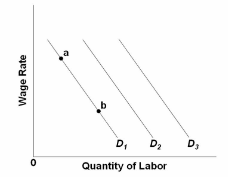
A. move from a to b on D 1 .
B. shift from D 2 to D 3 .
C. shift from D 3 to D 2 .
D. move from b to a on D 1 .
B. shift from D 2 to D 3 .
You might also like to view...
Suppose the United States exports cars to France and imports cheese from Switzerland. This situation suggests that
a. the United States has a comparative advantage relative to Switzerland in producing cheese, and France has a comparative advantage relative to the United States in producing cars. b. the United States has a comparative advantage relative to France in producing cars, and Switzerland has a comparative advantage relative to the United States in producing cheese. c. the United States has an absolute advantage relative to Switzerland in producing cheese, and France has an absolute advantage relative to the United States in producing cars. d. the United States has an absolute advantage relative to France in producing cars, and Switzerland has an absolute advantage relative to the United States in producing cheese.
Suppose that the labor market for life guards is initially in equilibrium. Then a new television series debuts which glamorizes the social opportunities for life guards. What happens to the equilibrium wage and quantity of life guards?
a. Both the equilibrium wage and quantity increase. b. Both the equilibrium wage and quantity decrease. c. The equilibrium wage increases, and the equilibrium quantity decreases. d. The equilibrium wage decreases, and the equilibrium quantity increases.
Consumption expenditures in the U.S. usually account for approximately __________ percent of GDP
A) 40 B) 50 C) 60 D) 70 E) 80
Regulation focused on the impact of production on the environment and society, the working conditions under which production occurs, or the physical attributes of goods, is known as
A) cost-of-service regulation. B) rate-of-return regulation. C) social regulation. D) monopoly regulation.