When a textile company keeps track of its inventory using a computer and its competitor uses a pad of paper and a pencil, they are both answering the ________ part of one of the two big economic questions
A) "what"
B) "how"
C) "for whom"
D) "where"
B
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. If demand shifts from D1 to D2, and at the same time, supply shifts from S1 to S2, then according to the figure: 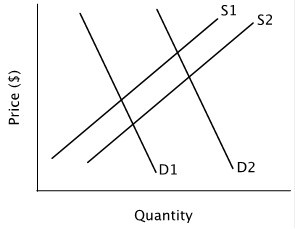
A. the equilibrium quantity will increase and the equilibrium price will increase. B. the equilibrium quantity will decrease and the equilibrium price will decrease. C. the equilibrium quantity will decrease and the equilibrium price will increase. D. the equilibrium quantity will increase and the equilibrium price will decrease.
Natural unemployment equals the sum of
A) cyclical and frictional unemployment. B) cyclical, business, and structural unemployment. C) frictional and structural unemployment. D) business and cyclical unemployment. E) cyclical and structural unemployment.
In the RBC model, an adverse supply shock causes the decrease in natural real GDP to be minimized when the labor supply curve is
A) downward sloping and extremely flat. B) upward-sloping and extremely flat. C) upward-sloping and extremely steep. D) vertical.
In the early 1960s, the discovery of the Phillips curve relationship caused economists and policy makers to think that they understood the trade-offs between: a. aggregate supply and aggregate demand. b. interest rate and investment. c. inflation and unemployment
d. monetary and fiscal policy. e. rule-making and discretionary policy.