The figure depicts a situation where:
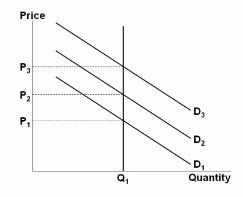
A. prices are sticky, but output is flexible.
B. prices are flexible, but output is constant.
C. prices and output are both flexible.
D. prices are sticky and output is constant.
A. prices are sticky, but output is flexible.
You might also like to view...
An increase in a consumer's income creates a
A) rightward parallel shift of the budget line. B) leftward parallel shift of the budget line. C) rightward rotation of the budget line, so that the budget line becomes steeper. D) leftward rotation of the budget line, so that the budget line becomes steeper.
Refer to Figure 14-2. If the government delays Gigacom's entry and Xenophone moves first, what is the likely outcome in the market?
A) Xenophone offers internet service via cable line and earns a profit of $4 million while Gigacom offers DSL internet service and earns a profit of $4.5 million. B) Both offer internet service via cable line; Xenophone earns a profit of $6 million and Gigacom earns a profit of $9 million. C) Both offer DSL internet service; Xenophone earns a profit of $8 million and Gigacom earns a profit of $7 million. D) Xenophone offers DSL internet service and earns a profit of $5 million while Gigacom offer internet service via cable line and earns a profit of $6.5 million.
Suppose there are two factories on a river, and both need clean water for their production processes. The upstream factory takes in clean water and dumps dirty water back into the river
The downstream firm must clean up the water it gets from the river before using it. In this situation A) the private costs of the downstream factory are more than the private costs of the upstream factory, but for both factories private costs and social costs are the same. B) the social costs are greater than the private costs for the upstream firm, while the social costs are less than the private costs for the downstream firm. C) the upstream factory's private costs are less than its social costs, and its external costs are borne by the downstream factory. D) the internal costs of the upstream factory are externalized by the downstream factory, which then passes them on to its customers.
When you are hungry, you receive the most satisfaction from the first apple and less satisfaction from each additional apple. What explains this?
a. income effect b. substitution effect c. law of elasticity of demand d. law of diminishing marginal utility