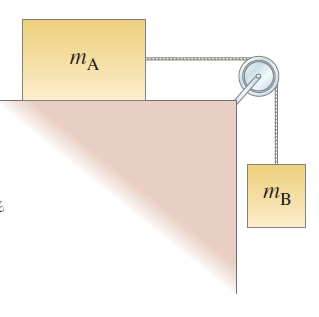
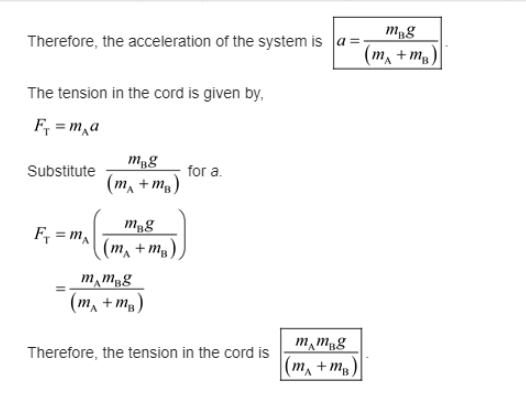
Figure 4–53 shows a block (mass mA) on a smooth horizontal surface, connected by a thin cord that passes over a pulley to a second block which hangs vertically.
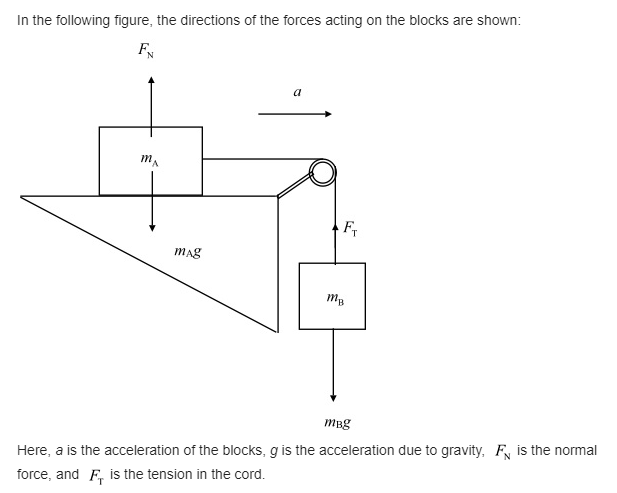
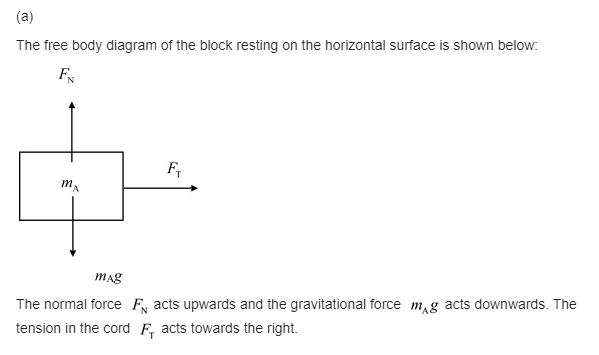
(a) Draw a free-body diagram for each block, showing the force of gravity on each, the force (tension) exerted by the cord, and any normal force.
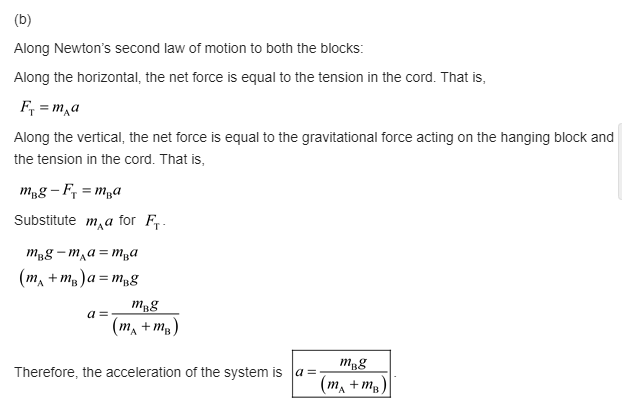
(b) Apply Newton’s second law to find formulas for the acceleration of the system and for the tension in the cord. Ignore friction and the masses of the pulley and cord.
Answer:

You might also like to view...
A +5.0-nC charge is at the point (0.00 m, 0.00 m) and a -2.0-nC charge is at (3.0 m, 0.00 m). What work is required to bring a 1.0-nC charge from very far away to point (0.00 m, 4.0 m)? (k = 1/4??0 = 9.0 × 109 N ? m2/C2)
A) 15 nJ B) 3.6 nJ C) 11 nJ D) 7.7 nJ
One of the most serious 3-D defects that affects the strength of ceramics is the presence of _____________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Greenhouse gases are opaque to _____
A) infrared radiation B) visible light C) ultraviolet radiation D) microwaves
What is the origin of synchrotron radiation in radio galaxies?
A. neutron stars at the center of the radio galaxy B. supernova explosions C. radiation from a massive black hole at the center of the galaxy D. high-speed electrons spiraling around the magnetic field lines E. hydrogen gas