A spacecraft can gain energy by passing near a planet
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
T
You might also like to view...
Might a region of intergalactic [between the galaxies] space, containing no material particles, contain energy?
A) No, because only material particles can possess energy. B) No, because physically nothing exists except particles and empty space. C) No, for both of the above reasons. D) Yes, it might contain the thermal energy of intergalactic gases. E) Yes, in the form of electromagnetic fields and other force fields.
The kinetic friction force that a horizontal surface exerts on a 60.0-kg object is 50.0 N. If the initial speed of the object is 25.0 m/s, what distance will it slide before coming to a stop?
A) 15.0 m B) 30.0 m C) 375 m D) 750 m
The term terminator refers to the boundary line dividing day and night on the surface of a planet or moon. In this experiment, it is the line between the bright and dark side of the Moon. State the phase of the Moon when the terminator is the (a) sunrise line, (b) sunset line
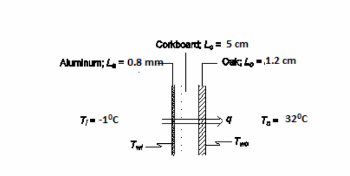
A composite refrigerator wall is composed of 5 cm of corkboard sandwiched between a 1.2 cm thick layer of oak and a 0.8 mm thick layer of aluminum lining on the inner surface. The average convective heat transfer coefficients at the interior and exterior wall are 11 and 8 W/(m2 K), respectively. (a) Draw the thermal circuit. (b) Calculate the individual resistances of the components of this composite wall and the resistances at the surfaces. (c) Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient through the wall. (d) For an air temperature of -1 0C inside the refrigerator and 32°C outside, calculate the rate of heat transfer per unit area through the wall.
GIVEN
• Refrigerator wall: oak, corkboard, and aluminum
• Thicknesses
? Oak (Lo) = 1.2 cm= 1.2*10-2 m
? Corkboard (Lc) = 5 cm= 5*10-2 m
? Aluminum (La) = 0.8 mm = 8*10-4 m
• Convective heat transfer coefficients
? Interior ( ci h ) = 12 W/(m2 K)
? Exterior ( co h ) = 8 W/(m2 K)
• Air temperature
? Inside (Ti) = -1°C
? Outside (To) = 32°C
FIND
(a) Draw the thermal circuit (b) The individual resistances (c) Overall heat transfer coefficient (U) (d) Rate of heat transfer per unit area (q/A)
ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional, steady state heat transfer
• Constant thermal conductivities
• Contact resistance between the different materials is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Oak (ko)= 0.19 W/(m K) at 20°C
Corkboard (kc) = 0.0415 W/(m K) at 20°C
Aluminum (ka) = 236 W/(m K) at 0°C