How is cross-price elasticity of demand used to determine whether two goods are substitutes or complements?
What will be an ideal response?
If the cross-price elasticity of demand for two goods is negative, then the two goods are complements. Two goods are considered substitutes if the cross-price elasticity of demand for the two goods is positive. Consider the following examples. Coffee and tea are substitutes. If the price of tea rises, I will buy more coffee and therefore, the cross price elasticity for tea and coffee is positive (the price of tea and the quantity of coffee always move in the same direction). Peanut butter and jelly are complements. If the price of peanut butter rises, I will eat fewer peanut butter and jelly sandwiches and therefore buy less jelly. This implies that the cross price elasticity for peanut butter and jelly is negative (the price of peanut butter and the quantity of jelly always move in opposite directions).
You might also like to view...
Use the following figure to answer the next question. 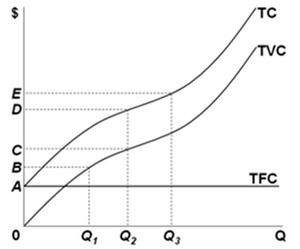 Total fixed cost at output level Q2 is measured by the vertical distance
Total fixed cost at output level Q2 is measured by the vertical distance
A. 0C. B. DE. C. AD. D. CD.
Macroeconomic topics include
A) total, nationwide employment. B) studying what factors influence the price and quantity of automobiles. C) studying the determination of wages and production costs in the software industry. D) the impact of government regulation of markets.
Since 1950, recessions in the United States
A) have become less severe than before 1950. B) have become more severe than before 1950. C) are about as severe as they were before 1950. D) have not occurred.
An speculator who buys a fifty-year corporate bond
A) must be expecting to still be alive in fifty years. B) is subject to substantial reinvestment risk. C) is probably expecting market interest rates to increase in the future. D) is probably expecting market interest rates to decrease in the future.