A 100 kg mass is blown apart into a 90.0 kg piece and a 10.0 kg piece. After the blast, the two masses are moving apart with a relative velocity of 100 m/s. The velocity of the 10.0 kg mass after the explosion is 90.0 m/s. The total kinetic energy of the two masses after the explosion is
A. 63,200 J.
B. 45,000 J.
C. 30,400 J.
D. 23,400 J.
E. 4,500 J.
B. 45,000 J.
You might also like to view...
How do we know how old the Sun is?
A) from radiometric dating of solar system meteorites B) from Newton's version of Kepler's third law and the orbits of the planets C) from calculating its fuel supply and how fast it is using it up D) from its speed and distance from us E) from radiometric dating of particles in the solar wind
A simple beam AB with an overhang BC is loaded as shown in the figure. The bending moment at the midspan of AB is approximately:
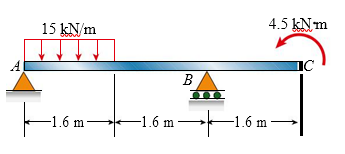
(A) 8 kN?m
(B) 12 kN?m
(C) 17 kN?m
(D) 21 kN?m
An object covers a distance of 8 meters in the first second of travel, another 8 meters during the next second, and 8 meters again during the third second. Its acceleration is
A) 0 m/s2. B) 5 m/s2. C) 8 m/s2. D) 24 m/s2.
To estimate the central temperature of the Sun, scientists ________
A) use hot gas to create a small Sun in a laboratory B) send probes to measure the temperature C) monitor changes in Earth's atmosphere D) use computer models to predict interior conditions