Using Figure 21.1, match the following:
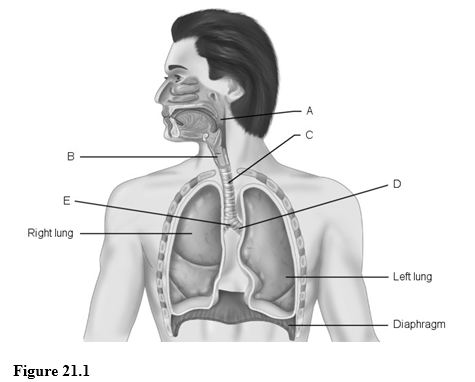
1) Main (primary) bronchus.
2) Pharynx.
3) Larynx.
4) Carina of trachea.
5) Trachea.
1) D
2) A
3) B
4) E
5) C
You might also like to view...
Acetylcholinesterase, monoamine oxidase (MAO), and catechol-O-methyltransferase are
A) neurotransmitters. B) enzymes that break down neurotransmitters. C) enzymes that act as neuromodulators. D) enzymes that could produce an EPSP. E) substances that could produce an IPSP.
In a lab, wave summation is demonstrated by increasing the ________ of the stimulus.
A. capacitance B. warm up time C. frequency D. intensity
Why does a pennate muscle generate more tension than does a parallel muscle of the same size?
A) A pennate muscle generates more tension because pennate muscle fibers lie parallel to the bone. B) A pennate muscle generates more tension because pennate muscle fibers lie perpendicular to the bone and parallel muscle fibers lie parallel to the bone. C) A pennate muscle generates more tension because a pennate muscle contains more muscle fibers than a parallel muscle. D) A pennate muscle generates more tension because a pennate muscle has a flat body and a parallel muscle has a broad body. E) A pennate muscle generates more tension because a pennate muscle pulls in only one direction and parallel muscles pull in different directions.
Norepinephrine and epinephrine are considered to be ________ when released into the bloodstream, but ________ when released at synapses
A) hormones; neurotransmitters B) neuropeptides; neurotransmitters C) neurotransmitters; hormones D) neurotransmitters; neuropeptides E) neuropeptides; neurohormones