Ultra-high-temperature sterilization effectively
A) reduces microbes that cause spoilage.
B) removes only mesophilic microbes.
C) reduces microbes that cause disease.
D) removes all microbes that cause diseases or spoilage.
E) reduces microbes that cause disease or spoilage.
D
Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Section: Physical Methods of Microbial Control
Learning Outcome: 9.13
You might also like to view...
What limits how big a cell can be?
a. Color b. Wavelength c. The surface area to volume ratio d. Resolution e. Type of electron microscopy.
A bacterium possessing a tuft of flagella at one end of its cell is called
a) amphitrichous. b) lophotrichous. c) monotrichous. d) peritrichous.
If the four cells shown resulted from cell division of a single cell with diploid chromosome number 2n = 4, what best describes what just occurred?
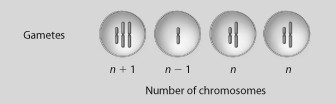
A) normal meiosis
B) translocation
C) inversion
D) nondisjunction
Which of the following is not needed in a reproductive cloning procedure?
A) an egg cell B) a sperm cell C) a surrogate mother D) a diploid cell