The place where the parent DNA molecule becomes unzipped for replication is called the ________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
replication fork
The place where the parent DNA molecule becomes unzipped for replication is called the replication fork.
You might also like to view...
A heptose contains how many carbon atoms?
A) 4 B) 5 C) 6 D) 7
A type III survivorship curve is characteristic of ____
a. dogs b. goats c. hawks d. clams e. horses
What is the key difference between photoheterotrophs and photoautotrophs?
a. Photoautotrophs only use bacteriochlorophyll; photoheterotrophs only use chlorophyll a. b. Photoheterotrophs produce oxygen as a by-product; photoautotrophs do not. c. Photoheterotrophs use hydrogen sulfide for reducing power; photoautotrophs do not. d. Photoheterotrophs use organic compounds as their carbon source; photoautotrophs use carbon dioxide as their carbon source.
What nucleotide change is a shared derived character for species A, B, and C, but not for species G?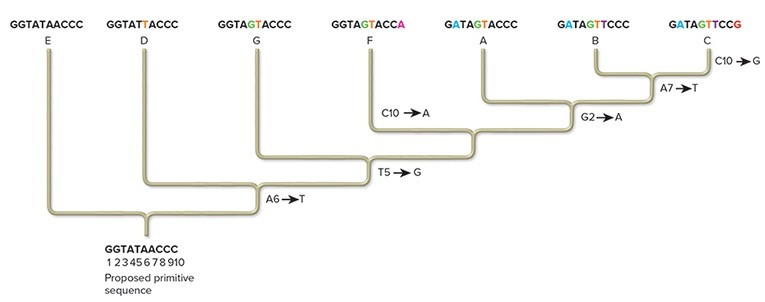 Note: A,T,G, and C refer to nucleotide bases, and the numbers refer to the position of the base in the nucleotide sequences.For example, A6 refers to an adenine at the sixth position.
Note: A,T,G, and C refer to nucleotide bases, and the numbers refer to the position of the base in the nucleotide sequences.For example, A6 refers to an adenine at the sixth position.
A. Changing the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G. B. Changing the second G to an A is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G. C. Changing the second G to an A and the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G. D. Changing the second G to a T is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G. E. None of these show a change in derived characteristics for A, B, and C that are not found in G.