The difference between quantity restrictions and price ceilings as to their effect on the market is that
A. while price ceilings are efficient, quantity restrictions are not.
B. while some consumers gain from price ceilings, no consumers gain from quantity restrictions.
C. only quantity restrictions make the market inefficient.
D. only price ceilings make the market inefficient.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Rather than prohibiting a good or service, the government might tax it. Imposing such a tax on a good or service ________ the equilibrium price and ________ the equilibrium quantity
A) raises; increases B) raises; decreases C) lowers; increases D) lowers; decreases
At a perfectly competitive firm’s short-run equilibrium level of output,
A. P = MR = MC. B. P = MR, but MR does not equal MC. C. P = MC, but MR does not equal MC. D. MR = MC and P < MR.
Will and Grace have adjoining unfenced back yards and each has just adopted a new puppy. Will values a fence between their yards at $250 and Grace values a fence between their yards at $200. The cost of building the fence is $300, which will be split equally if they both agree to build the fence. Therefore, their payoff matrix is as follows. 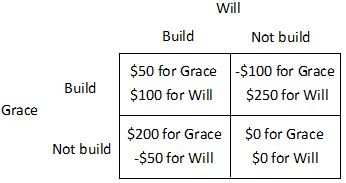 This game is a(n) ________ because ________.
This game is a(n) ________ because ________.
A. example of logrolling; both neighbors need to cooperate to provide the good. B. prisoner's dilemma; by playing their dominant strategy, both Will and Grace do worse than if they had both played their dominated strategy. C. inequitable situation; Grace does not value a fence as highly as does Will. D. tragedy of the commons; the backyard is treated as a common area by the puppies.
In a competitive market, the market demand is Qd = 60 - 6P and the market supply is Qs = 4P. A price ceiling of $3 will result in a
A. shortage of 15 units. B. surplus of 30 units. C. surplus of 12 units. D. shortage of 30 units.