Refer to the following figure. When price is $10 and quantity demanded is 2,000, what is the point elasticity of demand?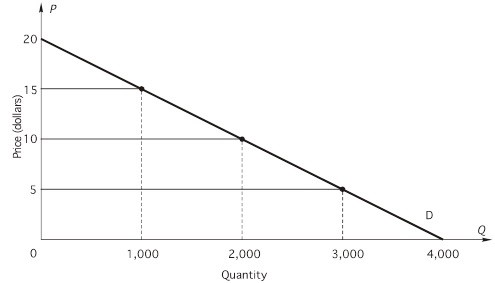
A. -1/3
B. -3
C. -5
D. -2/3
E. -1
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Sergio consumes only beef and snails and is maximizing his utility. If the price of beef is less than the price of snails, then we definitely know that
A) Sergio buys more beef than snails. B) Sergio buys more snails than beef. C) the marginal utility from the last pound of beef purchased is greater than the marginal utility from the last pound of snails purchased. D) the marginal utility from the last pound of snails purchased is greater than the marginal utility from the last pound of beef purchased.
Country A had a population of 1,000, of whom 600 worked an average of 8 hours a day and had a productivity of 2.5 . Country B had a population of 800, of whom 560 worked 8 hours a day and had productivity of 3.0 . Country
a. A had the higher level of real GDP and real GDP per person. b. A had the higher level of real GDP and Country B had the higher level of real GDP per person c. B had the higher level of real GDP and Country A had the higher level of real GDP per person d. B had the higher level of real GDP and real GDP per person.
Suppose that more British decide to vacation in the U.S. and that the British purchase more U.S. Treasury bonds. Ignoring how payments are made for these purchases,
a. the first action by itself raises U.S. net exports, the second action by itself raises U.S. net capital outflow. b. the first action by itself raises U.S. net exports, the second action by itself lowers U.S. net capital outflow. c. the first action by itself lowers U.S. net exports, the second action by itself raises U.S. net capital outflow. d. the first action by itself lowers U.S. net exports, the second action by itself lowers U.S. net capital outflow.
A country with a fixed exchange rate faces:
a. no monetary policy constraints in the long run. b. no monetary policy constraints in the short run. c. no monetary policy constraints in the long run and the short run. d. monetary policy constraints in the long run and the short run