Consider two economies: Barylia and Lithasia. The GDP per capita in Lithasia is $6,000 while the GDP per capita in Barylia is $12,000. Both countries grow exponentially at an annual rate of 10%
How will their GDPs vary over the next year? Is there any limitation of comparing the absolute levels of GDP per capita of both countries over the next years? If yes, what is a plausible solution?
The GDP per capita of Lithasia after one year will be $6,000 + $600 = $6,600.
The GDP per capita of Barylia after one year will be $12,000 + $1,200 = $13,200.
Initially, the gap between the GDP per capita of both countries was $12,000 - $6,000 = $6,000.
A year hence, the gap between the GDP per capita of both countries is $13,200 - $6,600 = $6,600.
Hence, over one year, the gap between the GDP per capita of both countries has increased by $600.
Ratio of GDP per capita of Barylia and Lithasia after one year = $13,200/$6,600 = 2 times.
Hence, even after a year, the GDP per capita of Barylia is twice that of Lithasia.
This implies that the relative GDPs of both nations have remained stable although the absolute gap has increased. Thus, comparing absolute levels of GDP per capita does not lead us to an accurate conclusion. In the presence of exponential growth, even though relative GDPs remain stable, the absolute gaps in the GDPs of both countries will increase. For this reason, a better statistic to be considered is the ratio of the GDP per capita rather than comparing the absolute levels of GDP per capita of both countries over time.
You might also like to view...
Zane's Vanes is a service that restores old weather vanes. Zane has just spent $125 purchasing a 1920s-era weather vane which he expects to restore and sell for $500 once the work is completed
After having spent $125, Zane realizes that he will need to spend an additional $200 on materials to complete the restoration. Alternatively, he can sell the weather vane without restoring it for $200. What is his marginal benefit if he sells the weather vane without restoring it? A) $75 B) $125 C) $200 D) $300
According to the table shown, the firm's marginal costs:
This table shows the total costs for various levels of output for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.
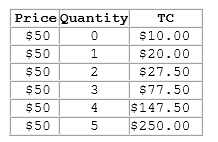
A. are constant.
B. increase as output increases.
C. decrease until the 2nd unit, then increase.
D. increase until the 4th unit, then decrease.
The limit on the amount of information a manager can comprehend about a firm's operation is known as
a. adverse selection b. bounded rationality c. diseconomies of scope d. managerial incompetence e. moral hazard
The possible measuring units for capital productivity could be units/$, Kg/Rial, Barrels/$, etc.
a. true b. false