In effect, an annuity provides insurance
a. against the risk of dying and leaving one's family without a regular income.
b. against the risk of living too long.
c. to people who are not risk-averse.
d. to people whose utility functions do not display the usual properties.
b
You might also like to view...
Chapter 15 suggests that the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) provides an example of
A) bad intentions and bad unintended consequences. B) good intentions and bad unintended consequences. C) bad intentions and good unintended consequences. D) good intentions and good unintended consequences.
Crowding out may occur because ________ fiscal policy usually involves the government ________ money.
A. expansionary; lending B. contractionary; borrowing C. contractionary; lending D. expansionary; borrowing
?Hair Pins /hourBandanas /hourNigel410Mia93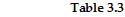 Consider two individuals, Nigel and Mia, who produce hair pins and bandanas. Nigel's and Mia's hourly productivity are shown in Table 3.3. Which of the following is true?
Consider two individuals, Nigel and Mia, who produce hair pins and bandanas. Nigel's and Mia's hourly productivity are shown in Table 3.3. Which of the following is true?
A. Nigel has a comparative advantage in producing hair pins but not bandanas. B. Nigel has a comparative advantage in producing bandanas but not hair pins. C. Nigel has a comparative advantage in producing both goods. D. Nigel does not have a comparative advantage in producing either good.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. One major tenet of behavioral economics is that the human brain is prone to commit errors in perception. 2. The low-energy mental shortcuts or heuristics that the human brain commonly employs is one major reason for the systematic errors in decision-making that people make which is the focus of behavioral economics. 3. One consequence of the confirmation bias is that many people believe that they could "beat the (stock) market". 4. When people often blame "act of nature" or their colleagues for their plans going awry, they are illustrating the cognitive bias known as the overconfidence effect. 5.When people change their decision just because the context of the given information is changed, we call that the framing effect.