Solve the problem.dy/dt = ky + f(t) is a population model where y is the population at time t and f(t) is some function to describe the net effect on the population. Assume k = .02 and 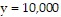 when t = 0. Solve the differential equation of y when f(t) = 9t.
when t = 0. Solve the differential equation of y when f(t) = 9t.
A. y = -450t - 22,500 + 32,500e-.02t
B. y = 450t - 22,500 + 32,500e-.02t
C. y = 450t + 22,500 + 32,500e-.02t
D. y = -450t - 22,500 + 32,500e.02t
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The following table shows the amount remaining, in grams, of a radioactive substance after t years.


A. Calculate the average rate of change in amount of radioactive substance from 

What will be an ideal response?
Solve the problem.An artist is creating a mosaic that cannot be larger than the space allotted which is 4 feet tall and 6 feet wide. The mosaic must be at least 3 feet tall and 5 feet wide. The tiles in the mosaic have words written on them and the artist wants the words to all be horizontal in the final mosaic. The word tiles come in two sizes: The smaller tiles are 4 inches tall and 4 inches wide, while the large tiles are 6 inches tall and 12 inches wide. If the small tiles cost $3.50 each and the larger tiles cost $4.50 each, how many of each should be used to minimize the cost? What is the minimum cost?
What will be an ideal response?
Determine whether the equation is a linear equation in two variables.x = 9
A. yes B. no
Find the zeros of the polynomial function and state the multiplicity of each.f(x) = (x + 2)2(x - 1)
A. -2, multiplicity 1; 1, multiplicity 1 B. 2, multiplicity 2; 1, multiplicity 1 C. -2, multiplicity 2; 1, multiplicity 1 D. -2, multiplicity 1; 1, multiplicity 2