A 2.0-kg object has a velocity of 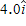 m/s at t = 0. A constant resultant force of
m/s at t = 0. A constant resultant force of 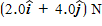 then acts on the object for 3.0 s. What is the magnitude of the object's velocity at the end of the 3.0-s interval?
then acts on the object for 3.0 s. What is the magnitude of the object's velocity at the end of the 3.0-s interval?
A. 9.2 m/s
B. 6.3 m/s
C. 8.2 m/s
D. 7.2 m/s
E. 7.7 m/s
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If a polymer is to be extruded at a high shear strain rate, which of the following material characteristics is most desirable?
(a) Shear thickening. (b) Newtonian fluid. (c) Shear thinning. (d) Elastic.
A 2.00-kg object traveling east at 20.0 m/s collides with a 3.00-kg object traveling west at 10.0 m/s. After the collision, the 2.00-kg object has a velocity 5.00 m/s to the west. How much kinetic energy was lost during the collision?
A) 0.000 J B) 458 J C) 516 J D) 91.7 J E) 175 J
Earth's core is
a. liquid. b. part solid and part liquid. c. solid. d. molten.
Determine the charge stored by C1 when C1 = 20 ?F, C2 = 10 ?F, C3 = 30 ?F, and V0 = 18 V
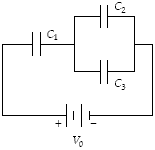
a.
0.37 mC
b.
0.24 mC
c.
0.32 mC
d.
0.40 mC
e.
0.50 mC