Describe the process by which DNS servers resolve a domain name. Include in your response a discussion of the DNS hierarchy. Provide an example of how this works.
What will be an ideal response?
ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers), through its agreement with the U.S. Department of Commerce, oversees the assignment of IP addresses, the accreditation of domain name registrars, and contracts with TLD (top-level domain) registries as part of the DNS. The DNS also consists of a hierarchy of servers used to translate domain names into IP addresses in a process called resolving the domain name.?At the top of the DNS hierarchy are the DNS root name servers that publish a directory of the next level of DNS servers, called the root zone file. The root zone file lists the addresses of all the TLD and ccTLD (country code top-level domain) DNS servers. Twelve different organizations, including VeriSign, NASA, the University of Maryland, and the University of Southern California, operate the root name servers.?At the next level are the DNS authoritative servers, which contain the IP information for the TLD and ccTLD domains and their registrants. At the bottom of the hierarchy are thousands of local DNS caching servers operated by ISPs and company IT departments containing stored domain name and IP address information developed from previous domain name resolution inquiries. The DNS namespace consists of all of the information in the DNS databases, including the top-level domain, country code top-level domain, domain name, and IP address information.?The process of resolving a domain name to an IP address begins with a local caching server, which may reside at your company or with your ISP. In most cases, a local caching server quickly can resolve a domain name to its IP address based on the server's cached or stored resolution inquiries. In some cases - for example, the first time the caching server attempts to resolve a specific domain name or if the caching server has just been started and its cache is empty - the caching server must contact authoritative or root name servers in the DNS to resolve a domain name.?Assume you have entered the URL mynewsite.biz in your browser. Your browser first contacts the local caching server to resolve the mynewsite.biz domain name to its IP address. If the local caching server cannot resolve the domain name, it can contact the authoritative server for the .biz TLD for a list of other authoritative servers that can resolve the mynewsite.biz domain name. The caching server then queries one of the appropriate authoritative servers for the mynewsite.biz domain and returns the IP address to the browser. If the caching server does not know the address for the .biz TLD authoritative server, it can contact a root name server for the address.
You might also like to view...
____________________ are used to enter data for processing.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
You can specify scaling to reduce or enlarge a worksheet for printing.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
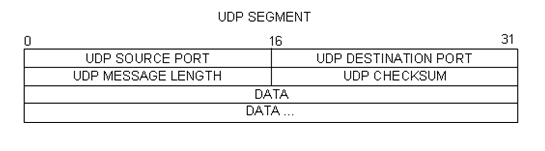
The figure below is a UDP datagram diagram. Header information is sparse, compared to the TCP datagram. Similar to TCP, each UDP datagram is identified by the UDP source port and UDP destination port.
Using the Wireshark capture of the first UDP datagram, fill in information about the
UDP header. The checksum value is a hexadecimal (base 16) value, denoted by the preceding
0x code:
Source IP address
Destination IP address
Source port number
Destination port number
UDP message length
UDP checksum
Which of the following is TRUE about PDF files?
A) A PDF can be opened, but cannot be edited in Word 2013. B) A PDF file can be opened and edited in Word 2013. C) It is a format developed by IBM. D) It is a format exclusive to Microsoft Word.