Refer to the graph shown for a small country that is a price taker internationally.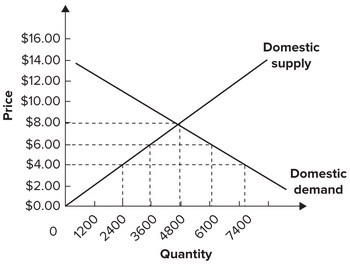 Assume the foreign supply of this product is perfectly elastic at a price of $4 per unit. To have the same effect on imports as a $2 per-unit tariff, the government would need to set an import quota of:
Assume the foreign supply of this product is perfectly elastic at a price of $4 per unit. To have the same effect on imports as a $2 per-unit tariff, the government would need to set an import quota of:
A. 2,500 units.
B. 5,000 units.
C. 1,200 units.
D. 1,300 units.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The marginal propensity to save is defined as
A) the change in saving divided by the change in disposable income. B) disposable income divided by saving. C) the change in disposable income divided by the change in saving. D) saving divided by disposable income.
The government is considering a mandatory savings program that forces people to save 8% of their income each year for retirement. What behavioral biases might be used as a justification for such a program? (Choose all that apply.) a. Limited cognitive ability, preventing people from being able to accurately estimate how much an investment early in one's career will grow. b. Limited willpower,
preventing people from being able to give up the pleasure of current consumption for the benefits of consumption later in retirement. c. Limited commitment power, leading the government to use the funds for current expenditures. d. Risk aversion, leading people to consume now rather than wait until the uncertain future.
The aggregate demand curve reflects:
a. a direct relationship between the price level in an economy and the real GDP demanded b. a direct relationship between real GDP demanded and total unemployment. c. an inverse relationship between the price level in an economy and the nominal GDP demanded. d. an inverse relationship between the price level in an economy and the real GDP demanded. e. an inverse relationship between the real GDP demanded and total unemployment.
Many members of Congress who represent urban low-income areas vote in favor of farm subsidies. In return, many representatives of agricultural areas support programs such as food stamps, which provide benefits for the urban poor. This situation would be an example of:
A. Confusing symptoms with causes B. Misguided subsidies C. Rent-seeking behavior D. Political logrolling