Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large increase in government purchases will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. expansionary; higher; potential
B. recessionary; higher; potential
C. recessionary; lower; lower
D. expansionary; higher; higher
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If a perfectly competitive firm is producing the short-run profit-maximizing quantity and is earning positive economic profits, the firm should anticipate ________.
A) the market equilibrium price to increase B) the market equilibrium price to decrease C) earning economic profits indefinitely D) the market supply to decrease
________ are costs that do not require a monetary payment.
A. Implicit costs B. Explicit costs C. Accounting costs D. All opportunity costs
Assuming that good "x" is measured on the x-axis and good "y" is measured on the y-axis, if the utility for the two goods "x" and "y" can be measured as U = y, then it can be concluded that
A) "x" and "y" are perfect complements. B) "x" is a "bad". C) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are upward sloping. D) the indifference curves on the x,y graph are horizontal.
Refer to the above table. If planned investments were fixed at $16, taxes were zero, government purchases of goods and services were zero, and net exports were zero, then equilibrium real GDP would be $630 initially. If government purchases were then raised from $0 to $4, other things constant, then the equilibrium real GDP would become:
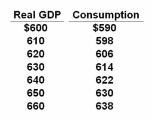
The table shows the consumption schedule for a hypothetical economy. All figures are in billions of dollars.
A. $660
B. $630
C. $640
D. $650