A firm pays Pam $40 per hour to assemble personal computers. Each day, Pam can assemble 4 computers if she works 1 hour, 7 computers if she works 2 hours, 9 computers if she works 3 hours, and 10 computers if she works 4 hours. Pam cannot work more than 4 hours day. Each computer consists of a motherboard, a hard drive, a case, a monitor, a keyboard, and a mouse. The total cost of these parts is $600 per computer. If Jane works for 6 hours she can rent out 9 apartments, and if she works for 7 hours she can rent out 12 apartments. The marginal benefit of Jane's 7th hour of work equals:
A. 9 apartments
B. 3 apartments
C. 1 apartment
D. 12 apartments
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose we examine how the consumer's optimum changes when the price of good X changes, while the consumer's tastes, income, and the price of all other goods are held constant. This procedure is used to derive
a. the Engel curve for good X. b. the (ordinary) demand curve for good X. c. the compensated demand curve for good X. d. the substitution and income effects for good X.
Which statement is most likely correct about quantity supplied?
a. When economists refer to quantity supplied, they are referring to a certain point on the supply curve or a certain quantity on the supply schedule. b. When economists refer to quantity supplied, they are referring to the relationship between a range of prices and the quantities supplied at those prices. c. Quantity supplied does not change with price. d. Quantity supplied will increase for one good when the quantity of the other good is increased.
Figure 11-2
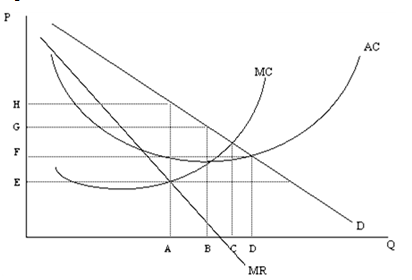
A. A B. B C. C D. D
An inflationary gap can be closed with
A) using an expansionary monetary policy. B) using a policy action such as a reduction in taxes. C) using a policy action such as a reduction in government purchases. D) imposing price controls to prevent prices from rising.