Two tiny beads, each of mass 3.2 g, carry equal-magnitude charges. When they are placed 6.4 cm apart and released in outer space, they begin to accelerate toward each other at 538 m/s2
What is the magnitude of the charge on each bead? (k = 1/4??0 = 9.0 × 109 N ? m2/C2 ) A) 510 nC
B) 44 nC
C) 1800 nC
D) 890 nC
E) 1300 nC
D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements about Pluto is true?
A) It has more in common with other icy objects in the Kuiper belt than it does with the jovian planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune). B) It is the most massive object that orbits the Sun beyond the orbit of Neptune. C) It is orbited by only one moon. D) It is the only object in our solar system that is categorized as a "dwarf planet."
Torques T 5 5.7 kN # m are applied to a hollow aluminum shaft (G 5 27 GPa and d1 5 52 mm). The allowable shear stress is 45 MPa and the allowable normal strain is 8.0 3 1024. The required outside diameter d2 of the shaft is approximately:
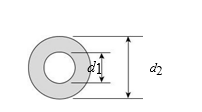
(A) 38 mm
(B) 56 mm
(C) 87 mm
(D) 91 mm
An air-filled capacitor stores a potential energy of due to its charge. It is accidentally filled with water in such a way as not to discharge its plates. How much energy does it continue to store after it is filled?
(The dielectric constant for water is 78 and for air it is 1.0006.) A) 0.077 mJ B) 468 mJ C) 0.040 mJ D) 6.00 mJ
Which color of visible light carries the most energy per photon?
A) red B) green C) blue D) violet E) all the same