Figure 2-5 shows five different combinations of rockets and cruise ships that a country could manufacture. The production possibilities frontier that is illustrated in Figure 2-5 exhibits
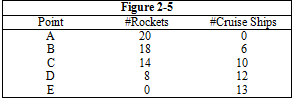
a. decreasing opportunity cost
b. increasing opportunity cost
c. constant opportunity cost
d. zero opportunity cost
e. heightened opportunity cost
b
You might also like to view...
In 2014, tire industry lobbyists pressured the United States government to consider imposing an additional tariff of up to 86% on top of the current 4% tariff on imported Chinese-made tires
This type of behavior where industry lobbyists attempt to influence law for their own economic advantage is called A) deadweight protection. B) blackmail. C) quota manipulation. D) rent seeking.
The above figure shows the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost curves of coffee in the nation of Kaffenia. When marginal social benefit is equal to the marginal social cost of coffee in Kaffenia
A) three hundred pounds per day will be produced and consumed. B) the efficient quantity of coffee is being produced and consumed. C) any decrease in coffee consumption or production would result in a deadweight loss. D) All of the above are correct.
Back to the text: Amar is a safekeeper of people's gold (their money). He is a smart businessman who does not gamble and keeps 20 percent of the deposited gold on reserve to handle the transactions demands of depositors. Amar holds to a sound
a. excess reserve depletion rate b. liquidity of money c. volatility of money d. fractional reserve rule e. quantity theory of money
When the Fed raises the discount rate, it
a. lowers the cost of borrowing from the Fed, allowing banks to make more loans b. raises the cost of borrowing from the Fed, disallowing banks from making the same quantity of loans c. increases the amount of excess reserves that banks hold, allowing them to make more loans d. increases the amount of excess reserves that banks hold, disallowing them from making the same quantity of loans e. decreases the amount of excess reserves that banks hold, disallowing them from making the same quantity of loans