If a = 3.0 mm, b = 4.0 mm, Q1 = ?60 nC, Q2 = 80 nC, and q = 30 nC in the figure, what is the magnitude of the electric force on q?
![]()
a.
1.4 N
b.
1.0 N
c.
1.7 N
d.
2.0 N
e.
0.50 N
b
You might also like to view...
Suppose you kick a soccer ball straight up to a height of 10 meters. Which of the following is true about the gravitational potential energy of the ball during its flight?
A) The ball's gravitational potential energy is greatest at the instant it returns to hit the ground. B) The ball's gravitational potential energy is greatest at the instant when the ball is at its highest point. C) The ball's gravitational potential energy is always the same. D) The ball's gravitational potential energy is greatest at the instant the ball leaves your foot.
George Gamow, the creator of the Big-Bang theory of the origin of the universe, asks you to imagine what would happen if the speed of light was 15. mi/h
If you were on the sidewalk looking at a bicyclist ride down the street, how does she look to you while riding, compared to when she stops? A) taller, the same mass, but stretched out like a limousine B) shorter, the same mass, but stretched out like a limousine C) same height, greater mass, and flatter in the direction she is moving D) same height, smaller mass, and flatter in the direction she is moving E) shorter, greater mass, but stretched out like a limousine
The velocity required to escape an astronomical body is known as the _______________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
The letter N is symmetric (in the sense defined in this chapter) for rotations around an axis going through its center that points in which of the following directions?
A. 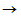
B. 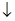
C. Perpendicular to the plane of the letter
D. A and C
E. A, B, and C