Figure 14-6
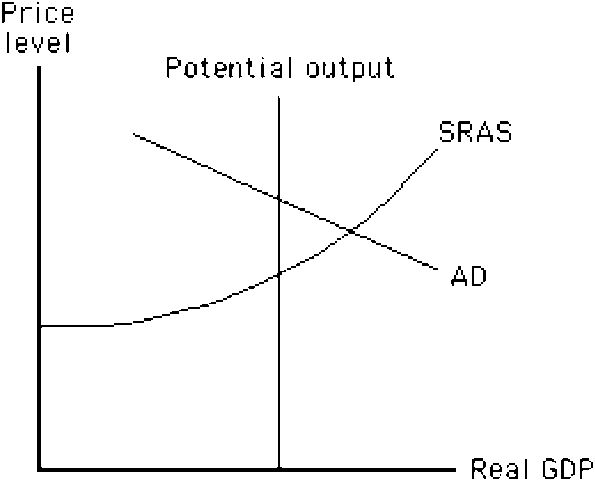
In the situation shown in , how could the Fed return the economy to potential output?
a.
decrease government spending
b.
increase taxes
c.
decrease taxes
d.
shift to a more restrictive monetary policy
e.
shift to a more expansionary monetary policy
d
You might also like to view...
The Federal Reserve cannot target both the money supply and the interest rate because it does not control
A) bank reserves. B) open market operations. C) money demand. D) the discount rate.
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, if a country's interest rate falls, then its
a. net capital outflow and its net exports rise. b. net capital outflow rises and its net exports fall. c. net capital outflow falls and its net exports rise. d. net capital outflow and its net exports fall.
Which of the following is one of the widely-acknowledged problems with the consumer price index (CPI) as a measure of the cost of living?
What will be an ideal response?
When inflation occurs
A. money gains in value. B. money loses value. C. the value of money is unaffected. D. the value of demand deposits falls but the value of currency is unaffected. E. inflation has nothing to do with money.