The price of good A goes up. As a result the demand for good B shifts to the left. From this we can infer that:
A) good A is a normal good.
B) good B is an inferior good.
C) goods A and B are substitutes.
D) goods A and B are complements.
E) none of the above
D
You might also like to view...
Tiebout local public good provision is more easily implemented than a Lindahl equilibrium -- because people know each other's tastes locally and can more easily come up with the right way to divide the cost for public goods.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
If the market for labor is perfectly competitive, the profit maximizing level of labor occurs where
A) MRPL < W (the wage). B) MRPL = P (the output price). C) MRPL just exceeds W. D) MRPL = W. E) none of the above
Comparisons of per capita GDP across international boundaries provide information on the distribution of GDP within each country.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
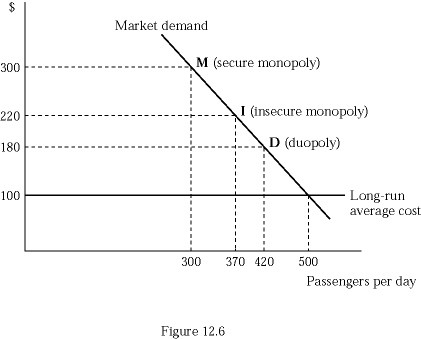 In Figure 12.6, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit maximizing price of $300 per ticket. What is Fly Smart's total profit as a secure monopoly?
In Figure 12.6, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit maximizing price of $300 per ticket. What is Fly Smart's total profit as a secure monopoly?
A. $60,000 B. $40,000 C. $44,400 D. $33,600