Explain how interest rates and bond prices are related to one another. Why is this important for monetary policy?
Interest rates and bond prices are inversely related; when one increases, the other automatically decreases. The reason for this is that bonds pay a specified amount of money per year as interest and this amount does not change after the bond has been issued. If bond prices fall, then the effective rate of interest increases since the payment amount remains the same. The relationship is important for monetary policy because the principal tool of monetary policy is the open market purchase and sale of government securities. When the Fed sells government securities (bonds) the price of bonds will fall, and therefore, interest rates would rise. The price of bonds has to fall to make the bonds attractive to buyers. Conversely, when the Fed purchases bonds, the price of bonds will be bid up and the effective rate of interest will fall. Higher interest rates are usually associated with a decrease in the money supply and lower interest rates are usually associated with increases in the money supply.
You might also like to view...
Can it be efficient for one trader to consume all units of the goods while the other trader consumes nothing? In other words, does this point lie on the contract curve?
What will be an ideal response?
A legal arrangement whereby a firm can hire only union labor is called
A) a union shop. B) a closed shop. C) a sweat shop. D) an open shop.
Corrective taxes are unlike most other taxes because they
a. distort incentives. b. move the allocation of resources away from the social optimum. c. raise revenue for the government. d. move the allocation of resources closer to the social optimum.
Suppose that a vaccine is developed for a highly contagious strain of flu. The likelihood that anyone will get this flu decreases as more people receive the vaccine. One of the demand curves below represents the private demand for the vaccine and the other represents the social demand for the vaccine.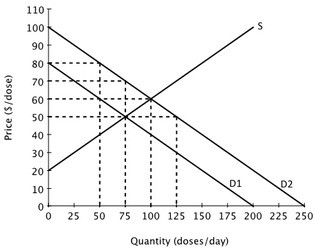 The private demand for the vaccine is given by ________, and social demand for the vaccine is given by ________.
The private demand for the vaccine is given by ________, and social demand for the vaccine is given by ________.
A. D2; MC B. D2; D1 C. D1; MC D. D1; D2