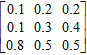When order effects occur such that experiencing condition A then condition B improves performance in B, but the reverse order doesn't help performance in A, this is an example of
a. asymmetric transfer.
b. order effects.
c. maturation effects.
d. latency effects.
A
You might also like to view...
Suppose a prime minister who runs a coalition government calls a snap election. Which statement describes the most likely reason for this action?
a. The prime minister wants to hand power to someone else in his or her own party. b. The prime minister has lost the support of many members of his or her own party. c. The prime minister expects his or her party to win a clear majority of seats in the new election. d. The prime minister hopes to strengthen the coalition by increasing his or her personal popularity.
Evaluate the extent to which the gender gap impacts voter behavior.
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is true of amicus curiae briefs?
A. They are used by interest groups to lobby courts B. They are used exclusively by liberal interest groups C. They are used exclusively by conservative interest groups D. They are now unconstitutional E. They are the means by which a litigant seeks Supreme Court review of a lower court decision
Determine whether the given matrix is stochastic.
?
?
A. No
B. Yes