 Figure 11.6Figure 11.6 depicts a monopolistically competitive firm in the long run. Illustrate on the graph the firm's price and output level in long-run equilibrium. Explain.
Figure 11.6Figure 11.6 depicts a monopolistically competitive firm in the long run. Illustrate on the graph the firm's price and output level in long-run equilibrium. Explain.
What will be an ideal response?
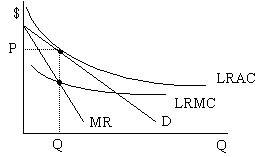
As illustrated on the graph, the firm picks the quantity at which its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost, shown as Q (this is the level of output at which the MR and LRMC curves intersect). It will charge price P for that level of output; P is the price associated with Q on the demand curve facing the firm.
You might also like to view...
Governments sometime create an excess supply of a product by setting a minimum price that is greater than the equilibrium price, resulting in a permanent excess supply of the product. This is known as a price ceiling
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Spot market is to futures market as
A) rice is to beans. B) today is to tomorrow. C) squares are to circles. D) quarters are to dollars.
Which of the following is a property of a forward contract?
a. In a forward contract cash is traded for immediate delivery. b. The buyer of a forward contract is "short" while the seller of the contract is "long". c. In a forward contract, the seller must own the commodity which is being traded. d. The value of future delivery depends on the market price of the commodity.
When sellers have more information about the quality of a good than buyers do, a relatively large share of the goods in the market will be low-quality goods. This is the ________ problem.
A. free-rider B. law of diminishing returns C. adverse selection D. moral hazard