Explain how the following factors affect the value of the dollar vis-à-vis other currencies under a floating exchange-rate system.a. Tariffs and quotas are placed by the U.S. government on all imports into the country.b. Demand by foreign consumers for the U.S. exports falls and the U.S. demand for imports rises.c. Rising interest rates in the United States relative to interest rates in Europed. Rising U.S. fiscal deficits reduce investor confidence and lead to capital outflows.
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE:
a. Tariffs and quotas placed by the U.S. on all imports into the country would decrease U.S. imports and thus decrease the demand for foreign currency. This, in turn, would lead to an appreciation of the dollar vis-à-vis other currencies.
b. By itself, decreased demand by foreign consumers for U.S. exports would decrease demand for U.S. dollars and lead to a depreciation of the dollar vis-à-vis other currencies. By itself, an increased U.S. demand for imports would increase demand for foreign currency, so, the foreign currency would appreciate and the dollar would depreciate. The two changes together therefore would depreciate the dollar.
c. Rising interest rates in the United States relative to interest rates in Europe leads to capital inflows. To invest in the United States, foreign investors would first have to purchase dollars in the foreign exchange market. This would increase the demand for dollars, thus appreciating the dollar vis-à-vis other currencies.
d. The capital outflows affect the foreign exchange market. Investors would have to sell dollars to buy foreign currency; thus, the supply of dollars would increase and the demand for foreign currencies would increase. The dollar, as a result, would depreciate vis-à-vis other currencies.
You might also like to view...
The "law of demand" refers to the fact that, other things remaining the same, when the price of a good rises,
A) the demand curve shifts rightward. B) the demand curve shifts leftward. C) there is a movement down along the demand curve to a larger quantity demanded. D) there is a movement up along the demand curve to a smaller quantity demanded. E) the demand curve shifts rightward and there is a movement up along the demand curve to a smaller quantity demanded.
The marginal cost of pollution abatement is represented by
A) an upward sloping curve. B) a downward sloping curve. C) a horizontal curve. D) a vertical curve.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.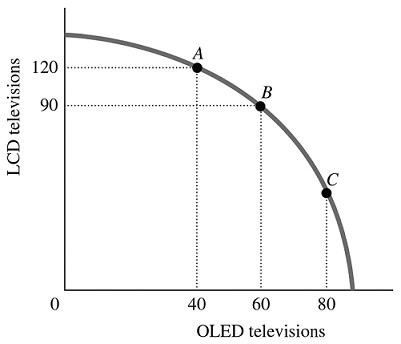 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy is currently at Point A. The opportunity cost of moving from Point A to Point B is the
A. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 60 additional OLED televisions. B. 90 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions. C. 30 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 20 additional OLED televisions. D. 120 LCD televisions that must be forgone to produce 40 additional OLED televisions.
When the price of a normal good falls, consumers buy a larger quantity because of the ________ effect and the ________ effect
A) substitution; income B) normal; inferior C) substitute; complement D) supply; demand