The advantage of an isoelastic demand curve is that:
A. both price and income elasticities are constant along the curve.
B. income elasticity is constant and price elasticity changes along the curve.
C. price elasticity is constant and income elasticity changes along the curve.
D. both price and income elasticity change along the curve.
A. both price and income elasticities are constant along the curve.
You might also like to view...
Though large firms have the knowledge and resources to utilize a better pricing strategy, many choose to use cost-plus pricing. One reason for this is that
A) large firms do not have to maximize their profits because they face little competition from other firms. B) firms often adjust the markup they charge to reflect current demand. C) there is less risk of violating antitrust laws if a cost-plus pricing strategy is used rather than a profit-maximizing pricing strategy. D) the additional revenue that would result from a profit-maximizing pricing strategy is an insignificant fraction of the firms' revenues.
The marginal factor cost for labor is
A. The net gain to a monopolist seller of labor if an additional unit of labor is hired. B. The demand for labor. C. The change in total costs that results from a one-unit increase in the quantity of a factor employed. D. The supply of labor.
Smith and Jones comprise a two-person economy. Their hourly rates of production are shown in the accompanying table. Calculators Per HourComputers Per HourSmith10010Jones1206 If Smith and Jones devote all of their resources to producing computers, then the maximum number of computers they can produce in an hour is:
A. 16. B. 10. C. 6. D. 120.
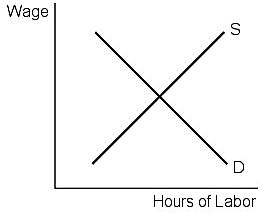
 In Figure 10.3, an increase in the supply of labor will cause the equilibrium:
In Figure 10.3, an increase in the supply of labor will cause the equilibrium:
A. wage and hours of labor used to increase. B. wage and hours of labor used to decrease. C. wage to increase and hours of labor used to decrease. D. wage to decrease and hours of labor used to increase.