In the early 2000s, some argued that the Indian government impeded foreign investment with tariffs, investment caps, and tons of red tape. In terms of promoting or retarding economic growth, such policies:
A. increase growth because they keep people producing for the local market.
B. decrease growth because they slow the growth of capital.
C. increase growth because they stop exploitation by foreigners.
D. decrease growth because they cause inflation.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Refer to the above figure. Suppose the original long-run equilibrium was at point B. What could have caused the move to the current equilibrium?
A) Aggregate demand must have decreased. B) Input prices must have increased, causing long-run aggregate supply to increase. C) Decreases in the price level caused short-run aggregate supply to fall. D) A temporary reduction in production due to bad weather.
Assuming all else equal, what is likely to happen to the demand curve for reserves in an economy if it goes through a period of rapid expansion?
A) There will be a n upward movement along the demand curve for reserves. B) The demand curve for reserves will shift to the left. C) There will be a downward movement along the demand curve for reserves. D) The demand curve for reserves will shift to the right.
The demand for computers increases. As a result
A) the quantity demanded of workers increases, the wage rate rises, and the supply of labor increases. B) the demand for workers increases, hiring increases, but wages stay the same since each firm faces a horizontal supply curve of labor. C) the wage rate increases in the industry and the quantity demanded of workers falls. D) the wage rate increases in the industry and the quantity supplied of workers increases.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.1 below to answer the question that follows.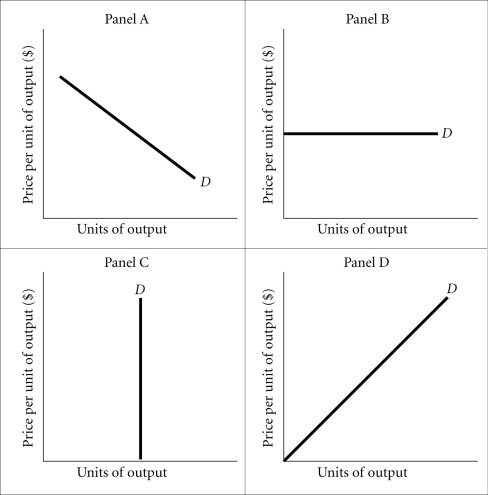 Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1. The demand curve facing an individual producer of wheat is most likely represented by
Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1. The demand curve facing an individual producer of wheat is most likely represented by
A. Panel A. B. Panel B. C. Panel C. D. Panel D.