Table 30.2Number of stylists (per week)Total output (per week)Marginal physical product (output per stylist)Total revenue (dollars per week)Marginal revenue product (dollars per stylist)00---________---160________________________280________________________390________________________490________________________Table 30.2 shows how many hairstyling appointments a hair salon can schedule per week based on the number of stylists. In the spaces provided, compute the marginal physical product (MPP) of the hair stylists, total revenue, and marginal revenue product of the stylists, assuming that a hair stylist charges $60 per appointment. What is the marginal physical product of the fourth hairstylist?
A. 0.
B. 22.5.
C. 90.
D. 5,400.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the below graphs. (Assume that the pre-migration labor force in Country A is 0d and that it is 0u in country B.) What part of domestic output in country B is the total wage bill or total wage income before and after the emigration?
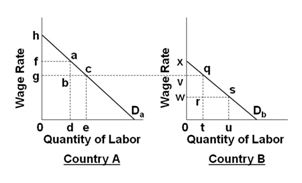
A. Area 0vqtand area 0wrt, respectively
B. Area 0vqt and area 0wsu, respectively
C. Area 0wsu and area 0vqt, respectively
D. Area 0wsu and area 0wrt, respectively
Which scenario will most likely happen as employers and employees increase their usage of the Internet in the job search process?
a. Job-related information will become more costly and cyclical unemployment will go up. b. Job-related information will become less costly and frictional unemployment will go up. c. Job-related information will become more costly and structural unemployment will go down. d. Job-related information will become less costly and frictional unemployment will go down.
Based on the following table, the additional cost of producing the 60th unit of output is: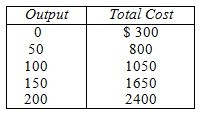
A. $5 B. $80 C. $250 D. $120 E. $8
An increase in investment and government purchases can be expected to shift the aggregate expenditures curve ________.
A. upward and the aggregate demand curve rightward B. downward and the aggregate demand curve leftward C. downward and the aggregate demand curve rightward D. upward and the aggregate demand curve leftward