What can you learn from soil and air temperature?
a. Soil temperature is an indicator of frozen ground status, driven partly by air temperature variability.
b. Soil temperature is an indicator of frozen water status, driven fully by air temperature variability.
c. Soil temperature is an indicator of heating ground status, driven fully by air temperature variability.
d. Soil temperature is an indicator of heating water status, driven partly by air temperature variability.
e. none of the above options are correct.
Answer is a. Soil temperature is an indicator of frozen ground status, driven partly by air temperature variability.
You might also like to view...
In which of the following locations in Canada does the greatest annual number of thunderstorms occur?
A. northern Saskatchewan B. southern Ontario C. northern Quebec D. northern Manitoba
With the Sun and Moon in this position, the side of the Earth facing the Moon experiences
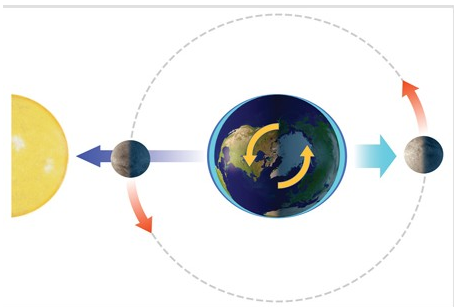
A) a normal high tide.
B) a normal low tide.
C) a spring tide.
D) a neap tide.
If the relative humidity is 100 percent and the environmental lapse rate is 8 degrees C per kilometer, then the air is conditionally unstable
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
How does the average depth of the oceans compare to the average elevation of the continents?
What will be an ideal response?