Describe the use of ATP molecules for energy
What will be an ideal response?
The source of energy for the body is the chemical energy stored in the carbon bonds of ingested food, but cells are not equipped to use this energy directly. Instead, the cells must extract energy from food nutrients and convert it into a form they can use, namely, the high-energy phosphate bonds of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which consists of adenosine with three phosphate groups attached. When the high-energy bond that binds the terminal phosphate to adenosine is split, a substantial amount of energy is released. ATP is the universal energy carrier -- the common energy "currency" of the body. Cells can "cash in" ATP to pay the energy "price" for running the cell machinery.
You might also like to view...
The function of the citric acid cycle is to
A) remove hydrogen atoms from organic molecules and transfer them to coenzymes. B) transfer the acetyl group gained from glycolysis to molecules of pyruvate. C) hydrolyze glucose in the presence of oxygen to obtain two pyruvate molecules. D) produce carbon dioxide to balance the oxygen requirement for cellular respiration. E) produce water.
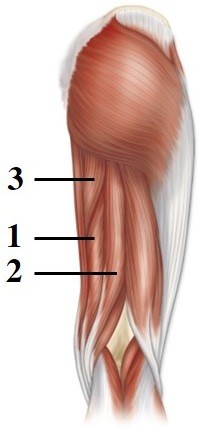 This figure shows a posterior view of the right thigh. What muscle does number 1 indicate?
This figure shows a posterior view of the right thigh. What muscle does number 1 indicate?
A. Semitendinosus B. Biceps femoris C. Adductor magnus D. Semimembranosus E. Gluteus maximus
Answer the following questions true (T) or false (F)
1. The cytosol and intracellular fluid (ICF) both refer to the fluid portion of the cytoplasm. 2. The fluid mosaic model defines the plasma membrane as a structure composed of multiple components, including the phospholipid bilayer, proteins, carbohydrates, and other lipids that exist in a dynamic arrangement. 3. During osmosis, the solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane from a solution with a higher solute concentration to a solution with a lower solute concentration.
Blood flow is greatest at the ________ of the lungs and perfusion is greatest at the ________ of the lungs.
A. base; base B. base; apex C. apex; apex D. apex; base