Although a monopoly can charge any price it wishes, it chooses:
a. the highest price.
b. price equal to marginal cost.
c. competitive prices.
d. a fair price.
e. the price that maximizes profit.
e
You might also like to view...
Suppose that a government agency is trying to decide between two pollution reduction policy options. Under the permit option, 100 pollution permits would be sold, each allowing emission of one unit of pollution. Firms would be forced to shut down if they produced any units of pollution for which they did not hold a permit. Under the pollution tax option, firms would be taxed $250 for each unit of pollution emitted. The regulated firms all currently pollute and face varying costs of pollution reduction, though all face increasing marginal costs of pollution reduction. Suppose the permit policy is adopted. A firm will wish to purchase its first permit if the price of that permit is less than or equal to:
A. the average cost of eliminating one unit of pollution. B. the reduction in costs associated with increasing its emissions from zero to one unit. C. the increase in costs associated with reducing its existing emissions by one unit. D. the lowest cost of eliminating one unit of pollution.
The figure below shows the supply and demand curves for oranges in Smallville. 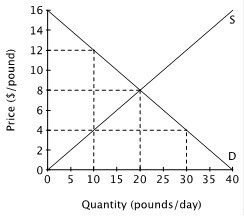 At the price of $4 per pound, sellers offer ________ pounds of oranges per day, and buyers want to purchase ________ pounds of oranges a day.
At the price of $4 per pound, sellers offer ________ pounds of oranges per day, and buyers want to purchase ________ pounds of oranges a day.
A. 30; 10 B. 20; 20 C. 10; 20 D. 10; 30
Which of the following is true for firms that produce in markets where there are no barriers to entry?
a. The firms will always make positive economic profits in the long run. b. The firms will always make positive economic profits in the short run. c. The firms will always make zero economic profits in the short run. d. The firms will always make zero economic profits in the long run.
What is one result of the Medicare subsidy?
A) The health care industry is more efficient than it otherwise would be. B) Patients may elect to have some treatments that are of low value to them but that are costly to provide. C) The elderly population in the United States receives a lower quality of medical care than what is provided for the elderly population in other countries. D) The number of physicians in the United States has declined.