What is risk management, and why is it important? Provide an example.
What will be an ideal response?
A risk is an event that could affect the project negatively. Risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, anticipating, and monitoring risks to minimize their impact on the project. Three important steps in risk management are:
• Develop a risk management plan. A risk management plan includes a review of the project’s scope, stakeholders, budget, schedule, and any other internal or external factors that might affect the project. The plan should define project roles and responsibilities, risk management methods and procedures, categories of risks, and contingency plans.
• Identify the risks. Risk identification lists each risk and assesses the likelihood that it could affect the project. The details would depend on the specific project, but most lists would include a means of identification, and a brief description of the risk, what might cause it to occur, who would be responsible for responding, and the potential impact of the risk.
• Analyze the risks. This typically is a two-step process: Qualitative risk analysis and quantitative risk analysis. Qualitative risk analysis evaluates each risk by estimating the probability that it will occur and the degree of impact. Project managers can use a formula to weigh risk and impact values, or they can display the results in a two-axis grid. For example, a Microsoft Excel XY chart can be used to display the matrix, as shown in Figure 3-29. In the chart, notice the various combinations of risk and impact ratings for the five sample values. This tool can help a project manager focus on the most critical areas, where risk probability and potential impact are high.
You might also like to view...
In its simplest form, project portfolio management can be broken down into four main components.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Answer the following questions with reference to how the ER model in Figure 17.13 maps to relational tables.
The ER diagram in Figure 17.13 shows only entities and primary key attributes. The absence of recognisable named entities or relationships is to emphasize the rule-based nature of the mapping rules described in Step 2.1 of logical database design.
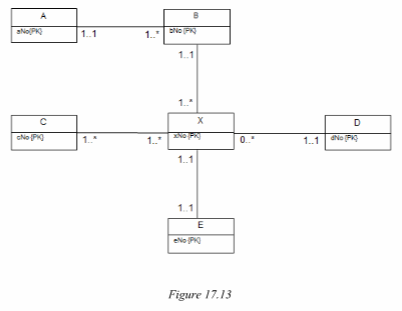
(a) How many relations will represent the ER model?
(b) How many foreign primary keys are mapped to the relation representing X?
(c) Which relation(s) will have no foreign key?
(d) Using only the letter identifier for each entity, provide appropriate names for the relations mapped from the ER model.
(e) If the cardinality for each relationship is changed to one-to-one with total participation for all entities; how many relations would be derived from this version of the ER model?
It is common, when preparing worksheets with financial information, that every cell displaying money is formatted in the Accounting Number Format
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Dramatic color and luminosity adjustments can be made in ____ color mode via the Image menu.
a. Lab b. Grayscale c. RGB d. CMYK