Prices for fresh fruit, vegetables and other food products are examples of
A) custom prices. B) sticky prices. C) temporary prices. D) auction prices.
D
You might also like to view...
Figure 1-2
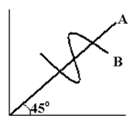
A. A—zero, B—one. B. A—one, B—zero. C. A—one, B—different at different points. D. A—different at different points, B—zero.
Does a change in the real interest rate shift the supply of loanable funds curve? Explain your answer
What will be an ideal response?
The division of labor means that:
A. labor markets are geographically segmented. B. unskilled workers outnumber skilled workers. C. workers specialize in various production tasks. D. each worker performs a large number of tasks.
The substitution effect argues that a consumer
A) will always use the additional purchasing power from a price decrease to purchase more of both goods. B) will not purchase more of a good when its price falls. C) will purchase more of a good that has become relatively cheaper, and less of a good that has become relatively more expensive. D) will purchase less of both goods if his or her real income increases.