When a market is in equilibrium
A) everyone has all they want of the commodity in question.
B) there is no shortage and no surplus at the equilibrium price.
C) the number of buyers is exactly equal to the number of sellers.
D) the supply curve has the same slope as the demand curve.
B
You might also like to view...
Refer to Game Matrix III. Which of the following is a property of this game?
Game Matrix III
The following questions refer to the game matrix below. Each firm has a choice of advertising, Ads, or not advertising, No ad. The profits each gets depend upon which it chooses.
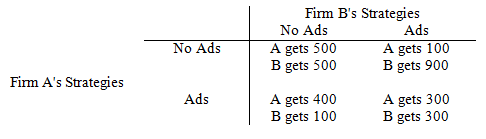
a. Both firms have dominant strategies.
b. There is no pure strategy Nash equilibrium.
c. There is a Nash equilibrium and it is Pareto optimal.
d. There is a Nash equilibrium and it is not Pareto optimal.
Between 1999 and 2007, the behavior of firms in the trucking industry closely matched the outcome predicted by the model of perfect competition
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The theory of public choice suggests that
A) government agencies tend to be inefficient because the people running them do not understand the concept of opportunity cost. B) government agencies tend to be inefficient because they are subject to institutional arrangements in which managers do not have an incentive to be efficient. C) the goods provided by government, whether public or private goods, are not scarce. D) you can lower your tax bill if you are careful not to consume too many government resources, regardless of what your neighbors do.
A dominant strategy:
A. exists in every game. B. is the best one to follow no matter what strategy other players choose. C. is always the same for all players of a game. D. awards the highest achievable payoff in a game.