Gauss's Law: Gaussian surfaces A and B enclose the same positive charge +Q. The area of Gaussian surface A is three times larger than that of Gaussian surface B. The electric flux through Gaussian surface A is
A. nine times larger than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B.
B. three times larger than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B.
C. equal to the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B.
D. three times smaller than the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B.
E. unrelated to the flux of electric field through Gaussian surface B.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Current: How much charge must pass by a point in a wire in 10 s for the current in the wire to be 0.50 A?
A. 20 C B. 2.0 C C. 5.0 C D. 0.050 C
Coil 1, connected to a 100-? resistor, sits inside coil 2. Coil 1 is connected to a source of 60 cycle per second AC current. Which statement about coil 2 is correct?
A. No current will be induced in coil 2. B. DC current (current flow in only one direction) will be induced in coil 2. C. AC current (current flow in alternating directions) will be induced in coil 2. D. DC current will be induced in coil 2, but its direction will depend on the initial direction of flow of current in coil 1. E. Both AC and DC current will be induced in coil 2.
A 3.00-kg ball has zero potential and kinetic energy. Maria drops the ball into a 10.0-m-deep well. After the ball comes to a stop in the mud, the sum of its potential and kinetic energy is:
a. zero. b. 294 J. c. ?294 J. d. 588 J. e. ?588 J.
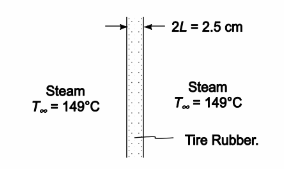
In the vulcanization of tires, the carcass is placed into a jig and steam at 149°C is admitted suddenly to both sides. If the tire thickness is 2.5 cm, the initial temperature is 21°C, the heat transfer coefficient between the tire and the steam is 150 W/(m2 K), and the specific heat of the rubber is 1650 J/(kg K), estimate the time required for the center of the rubber to reach 132°C.
GIVEN
• Tire suddenly exposed to steam on both sides
• Steam temperature (T?) = 149°C
• Tire thickness (2L) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Initial tire temperature (To) = 21°C
• The heat transfer coefficient (hc) = 150 W/(m2 K)
• The specific heat of the rubber (c) = 165 J/(kg K)
FIND
• The time required for the central layer to reach 132°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• Shape effects are negligible, tire can be treated as an infinite plate
SKETCH