Two countries engaged in trade in products with no scale economies, produced under conditions of perfect competition, are likely to be engaged in
A) inter-industry trade.
B) monopolistic competition.
C) intra-industry trade.
D) Heckscher-Ohlin trade.
E) oligopolistic competition
A
You might also like to view...
A producer's minimum acceptable price for a particular unit of a good
A. will, for most units produced, equal the maximum that consumers are willing to pay for the good. B. is the same for all units of the good. C. must cover the wages, rent, and interest payments necessary to produce the good but need not include profit. D. equals the marginal cost of producing that particular unit.
Refer to Figure 22.2 below. Suppose that the supply of land is constant at L acres, and Price per acre is $400. In addition, the before-tax demand for land can be characterized by the equation P = 500 - 2L, where L is the acres of land and P is the price.
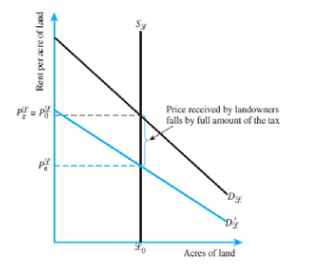
(A) What is the constant supply of land (L) in the market?
(B) If the after-tax demand curve, P , can be written as P = 400 - 4L, what is P , and how
much tax revenue is generated?
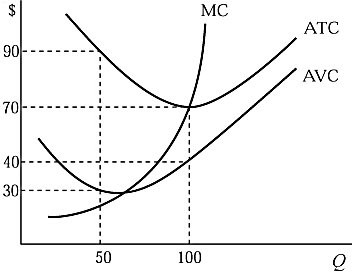
 Figure 5.4 shows a firm's marginal cost, average total cost, and average variable cost curves. At Q = 50, the total variable cost is:
Figure 5.4 shows a firm's marginal cost, average total cost, and average variable cost curves. At Q = 50, the total variable cost is:
A. $1,200. B. $1,500. C. $2,100. D. $2,800.
In the Keynesian model, suppose the Fed sets a target for the money supply. If the IS curve shifts to the left, and the Fed wants to keep output unchanged, what should the Fed do?
A. Reduce taxes. B. Increase taxes. C. Reduce the money supply. D. Increase the money supply.