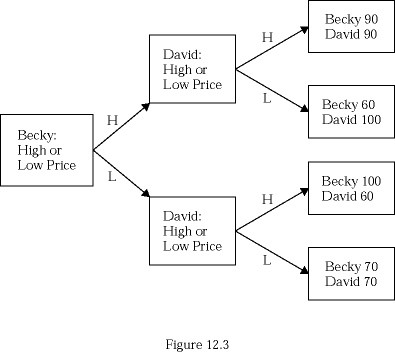
 Consider Figure 12.3. Choosing a high price is:
Consider Figure 12.3. Choosing a high price is:
A. a dominant strategy for David but not for Becky.
B. a dominant strategy for Becky but not for David.
C. a dominant strategy for both David and Becky.
D. not a dominant strategy for either David or Becky.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Demand for a product is given by Q = 100 - P and supply is given by Q = P - 10. If the quantity demanded rises by 10 units at every possible price, then the equilibrium price will
a. increase by $5 b. increase by $10 c. decrease by $5 d. increase by $7.50
Nancy's utility of wealth curve is given in the above figure. She is faced with a risky proposition which yields an income of $50 one-third of the time, $100 one-third of the time, and $150 one-third of the time. Her expected utility is
A) 100. B) 140. C) 150. D) 420.
On the graph above, the wage level at point ________ might represent an efficiency wage
A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 5
A $10,000 ten-year bond was issued at an interest rate of 6%. Carla is thinking about buying this bond one year before the end of the ten years, but interest rates are now 9%. What is the maximum amount that Carla should pay for this bond?
a. $9,174.31 b. $9,378.25 c. $8,982.43 d. $9, 764.20