The rational expectations theory indicates that expansionary policy will:
A. stimulate real output in the long run but not in the short run.
B. expand real output and employment if the public quickly anticipates the effects of the expansionary policy.
C. equalize real and nominal interest rates during lengthy periods of inflation.
D. fail to increase employment because individuals will anticipate it and take actions that will offset its impact.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency is called the
A) exchange rate. B) interest rate. C) Dow Jones industrial average. D) prime rate.
Assume initially this firm is at point A. The following would be a reason for a movement to point B. 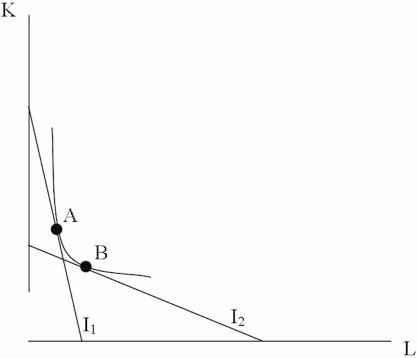
A. Wages go up and per unit capital costs go up. B. Both wages and per unit capital costs go down. C. Output decreases. D. Wages go down and per unit capital cost go up.
Which of the following definitely means productivity has increased?
A. Less output from fewer workers. B. Less output from more workers. C. More output from more workers. D. More output from fewer workers.
Real standards of living can increase
A. if there is positive growth in the manufacturing sector. B. if the country is producing the same amount they traditionally have and are enjoying more leisure time. C. only if there is positive economic growth. D. only at the cost of increased urban congestion.